Introduction to Blackbody Radiation
What is a Blackbody?
A blackbody is a theoretical perfect absorber and emitter of electromagnetic radiation. It absorbs 100% of all incident radiation regardless of wavelength and angle of incidence. When in thermal equilibrium, it emits radiation with a characteristic spectrum that depends only on its temperature.
Real objects approximate blackbodies to varying degrees. Carbon in graphite form absorbs all but about 3% of incoming radiation, making it an excellent approximation. Stars, including our Sun, behave approximately as blackbodies for many purposes.
The Physics of Thermal Radiation
All objects with temperature above absolute zero emit electromagnetic radiation due to the thermal motion of charged particles within them. The spectrum of this radiation follows fundamental physical laws.
Planck's Law
Max Planck derived the spectral radiance of a blackbody in 1900, solving the "ultraviolet catastrophe" that plagued classical physics:
where:
- = spectral radiance (W⋅sr⁻¹⋅m⁻³)
- = Planck's constant (6.626 × 10⁻³⁴ J⋅s)
- = speed of light (3 × 10⁸ m/s)
- = wavelength (m)
- = Boltzmann constant (1.381 × 10⁻²³ J/K)
- = absolute temperature (K)
Wien's Displacement Law
The wavelength at which a blackbody emits maximum intensity is inversely proportional to its temperature:
where KaTeX can only parse string typed expression m⋅K (Wien's displacement constant)
Stefan-Boltzmann Law
The total power radiated by a blackbody is proportional to the fourth power of its temperature:
where KaTeX can only parse string typed expression W⋅m⁻²⋅K⁻⁴ (Stefan-Boltzmann constant)
Interactive Blackbody Spectrum Visualization
Explore how temperature affects the blackbody radiation spectrum. The red dot indicates the peak wavelength according to Wien's displacement law.
Key Characteristics
- Perfect absorber: Absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation
- Perfect emitter: Emits maximum possible radiation at each temperature
- Lambertian surface: Radiation is emitted uniformly in all directions
- Temperature dependent: Spectrum depends only on temperature, not material
- Continuous spectrum: Emits radiation at all wavelengths
Historical Context and Quantum Revolution
The study of blackbody radiation was crucial to the development of quantum mechanics. Classical physics predicted the "ultraviolet catastrophe" - infinite energy emission at short wavelengths, which contradicted experimental observations.
The Ultraviolet Catastrophe
According to classical physics (Rayleigh-Jeans law), the energy density should be:
This predicts infinite energy as wavelength approaches zero, which is physically impossible.
Planck's Quantum Solution
Planck solved this by proposing that electromagnetic energy is quantized in discrete packets:
This quantization naturally explains the observed blackbody spectrum and marked the birth of quantum theory.
Experimental Evidence and Applications
Laboratory Blackbodies
Perfect blackbodies don't exist in nature, but excellent approximations can be created:
- Cavity radiator: A small hole in a hollow cavity acts as a near-perfect blackbody
- Carbon nanotubes: Absorb over 99.9% of incident light
- Vantablack: Absorbs 99.965% of visible light
Astronomical Applications
Blackbody radiation is fundamental to understanding stellar physics:
- Stellar temperatures: Determined from peak wavelength using Wien's law
- Cosmic microwave background: Remnant radiation from the Big Bang (T ≈ 2.7 K)
- Solar constant: Earth receives ~1361 W/m² from the Sun's ~5778 K blackbody radiation
Practical Applications
- Incandescent lighting: Tungsten filaments approximate blackbodies
- Thermal imaging: Infrared cameras detect blackbody radiation from objects
- Temperature measurement: Pyrometers use blackbody principles
- Solar energy: Understanding solar spectrum for photovoltaic efficiency
Black Body Radiation Curves
Single Temperature Analysis (5800K)
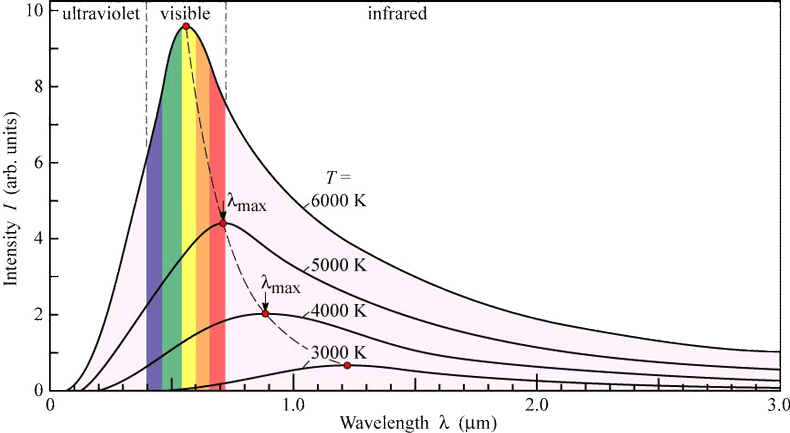
Fig 1. Black Body Radiation Plot at 5800K (Solar Temperature)
At 5800K (approximately the Sun's surface temperature), the peak wavelength is about 500 nm, which corresponds to green light. This is why the Sun appears white - it emits strongly across the entire visible spectrum.
Temperature Variation Analysis

Fig 2. Black Body Radiation Curves at Various Temperatures
Mathematical Relationships and Derivations
Energy Density
The energy density of blackbody radiation per unit wavelength interval is:
Photon Number Density
The number of photons per unit volume per unit wavelength interval:
Connection to Thermodynamics
Blackbody radiation pressure is related to energy density:
Related Topics
- Quantum Physics Overview
- Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
- Stellar Spectroscopy
- Thermal Physics